Implementing Data Structures Using JavaScript
January 11, 2021 • ☕️ 4 min read

本文将用js来实现常见的数据结构, 废话不多说, 直接开始吧~
Stack
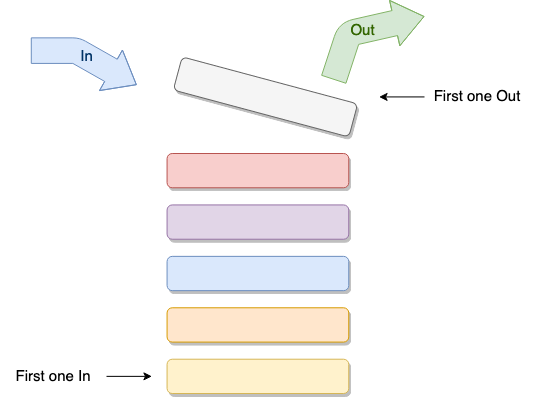
栈是一种遵从先进后出(first in last out, FILO)原则的有序集合。新添加或待删除的元素都保存在栈的同一端, 称作栈顶,另一端就叫栈底。
class Stack {
constructor() {
this._count = 0
// 如果用数组用来模拟栈的话, 其插入删除的时间复杂度为O(n), 而用object的话, 则为O(1)
this._items = {}
}
// 入队
push(element) {
this._items[this._count] = element
this._count++
}
// 出队
pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined
}
this._count--
const result = this._items[this._count]
delete this._items[this._count]
return result
}
// 访问栈顶
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined
}
return this._items[this._count - 1]
}
isEmpty() {
return this._count === 0
}
clear() {
this._count = 0
this._items = {}
}
size() {
return this._count
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return ''
}
let str = this._items[0]
for (let i = 1; i < this._count; i++) {
str += `,${this._items[i]}`
}
return str
}
}Queue
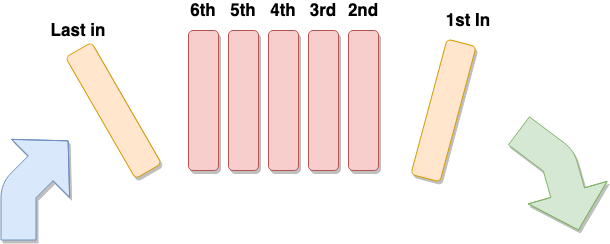
队列是遵循先进先出(first in first out, FIFO)原则的一组有序的项。队列在尾部添加新元素, 并从顶部移除元素。最新添加的元素必须排在队列的末尾。
class Queue {
constructor() {
this._items = {}
this._count = 0 // 总量 (注意, 出队不减少该量)
this._lowestCount = 0 // 队首的索引
}
// 入队
enqueue(element) {
this._items[this._count] = element
this._count++
}
// 出队
dequeue() {
if (this.isEmpty()) return
const result = this._items[this._lowestCount]
delete this._items[this._lowestCount]
this._lowestCount++
return result
}
// 访问队首
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) return
return this._items[this._lowestCount]
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0
}
size() {
return this._count - this._lowestCount // 记录总量 - 队首 = 现存个数
}
clear() {
this._items = {}
this._count = 0
this._lowestCount = 0
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) return ''
let str = this.peek() + ''
for (let i = this._lowestCount + 1; i < this._count; i++) {
str += `,${this._items[i]}`
}
return str
}
}Linked List
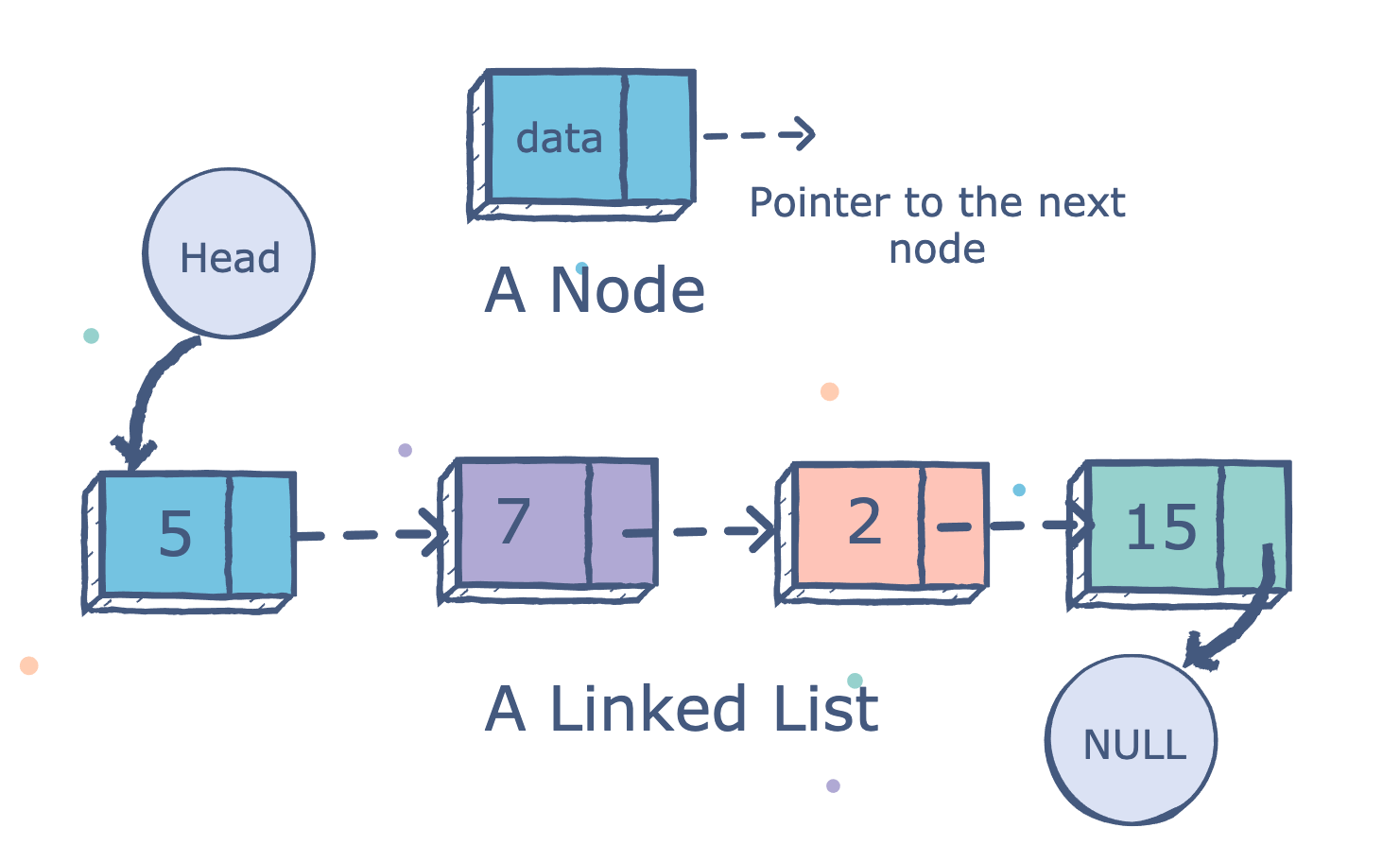
链表存储有序的元素集合, 但不同于数组, 链表中的元素在内存中并不是连续放置的。每个元素由一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的引用(也称指针或链接)组成。
// 链表的元素组成
class Node {
constructor(element) {
this.element = element
this.next = undefined
}
}
// 链表
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.count = 0
this.head = undefined
this.equalsFn = function (a, b) {
return a === b
}
}
push(element) {
const node = new Node(element)
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node
} else {
let current = this.head
while (current.next) { // 找到链表的最后一项
current = current.next
}
current.next = node
}
this.count++
}
instert(element, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new Node(element)
if (index === 0) {
const current = this.head
node.next = current
this.head = node
} else {
const prev = this.getElementAt(index - 1)
const current = prev.next
prev.next = node
node.next = current
}
this.count++
return true
}
return false
}
remove(element) {
const index = this.indexOf(element)
return this.removeAt(index)
}
indexOf(element) {
let current = this.head
for (let i = 0; i < this.count; i++) {
if (this.equalsFn(current.element, element)) {
return i
}
current = current.next
}
return -1
}
removeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
let current = this.head
if (index === 0) {
this.head = current.next
} else {
let prev = this.getElementAt(index - 1)
current = prev.next
prev.next = current.next
}
this.count--
return current.element
}
return undefined
}
getElementAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
let node = this.head
for (let i = 0; i < index && node; i++) {
node = node.next
}
return node
}
return undefined
}
getHead() { return this.head }
isEmpty() { return this.size() === 0 }
size() { return this.count }
clear() {
this.head = undefined
this.count = 0
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) return ''
let str = this.head.element
let current = this.head
for (let i = 0; i < this.count - 1; i++) {
current = current.next
str += ',' + current.element
}
return str
}
}Hash Table
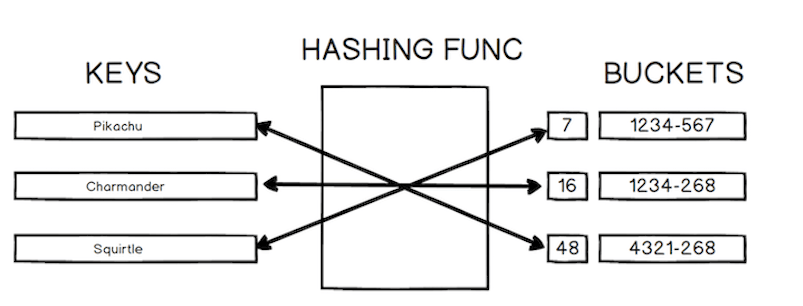
哈希表,是根据关键码值而直接进行访问的数据结构。
也就是说,它通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。这个映射函数叫做散列函数,存放记录的数组叫做散列表。
给定表M,存在函数f(key),对任意给定的关键字值key,代入函数后若能得到包含该关键字的记录在表中的地址,则称表M为哈希(Hash)表,函数f(key)为哈希(Hash) 函数。
class ValuePair {
constructor(key, value) {
this.key = key
this.value = value
}
toString() {
return `[${this.key}: ${this.value}]`
}
}
class HashTable {
constructor() {
this.toStrFn = function (item) {
if (item === null) {
return 'NULL'
} else if (item === undefined) {
return 'UNDEFINED'
} else if (typeof item === 'string' || item instanceof String) {
return `${item}`
}
return item.toString()
}
this.table = {}
}
djb2HashCode(key) {
// 最受社区推崇的散列函数之一, 极大减少了key冲突的概率
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key)
let hash = 5381
for (let i = 0; i < tableKey.length; i++) {
hash = hash * 33 + tableKey.charCodeAt(i)
}
return hash % 1013
}
hashCode(key) {
// 获取哈希值
return this.djb2HashCode(key)
}
put(key, value) {
if (key != null && value != null) {
const position = this.hashCode(key)
if (this.table[position] == null) {
this.table[position] = new LinkedList() // 借用上面实现过的链表
}
this.table[position].push(new ValuePair(key, value)) // 用哈希值作为key, 指向一个链表 (用于防止hash冲突)
return true
}
return false
}
get(key) {
const position = this.hashCode(key)
const linkedList = this.table[position]
if (linkedList != null && !linkedList.isEmpty()) {
let current = linkedList.getHead()
while (current != null) {
if (current.element.key === key) { // 由于存在hash冲突, 所为需要对比原本的key用于正确的返回其对应的值
return current.element.value
}
current = current.next
}
}
return undefined
}
remove(key) {
const position = this.hashCode(key)
const linkedList = this.table[position]
if (linkedList != null && !linkedList.isEmpty()) {
let current = linkedList.getHead()
while (current != null) {
if (current.element.key === key) {
linkedList.remove(current.element)
if (linkedList.isEmpty()) {
delete this.table[position]
}
return true
}
current = current.next
}
}
return false
}
getTable() {
return this.table
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0
}
size() {
return Object.keys(this.table).length
}
clear() {
this.table = {}
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return ''
}
const keys = Object.keys(this.table)
let objString = `{${keys[0]} => ${this.table[keys[0]].toString()}}`
for (let i = 1; i < keys.length; i++) {
objString = `${objString},{${keys[i]} => ${this.table[
keys[i]
].toString()}}`
}
return objString
}
}其他
树(Tree) 和 图(Graph)这两个能展开来讲的实在太多了, 受篇幅所限, 以后找机会拎出来单独写吧, 先摸了~
Referencing :
<< Learning JavaScript Data Structures and Algorithms, Third Edition >>